Ultimate Safety Guide


Introduction
This guide’s aim is to help you understand the main risks you might face in the crypto environment and teach you how to avoid common mistakes. We’ll cover different types of wallets, the dangers of Permit2, phishing attacks, scams via Telegram and X (ex-Twitter), rug pulls, honeypot tokens, and how seed phrases can be stolen via OneDrive. By the end, you’ll be much better equipped to protect your assets, as even small actions can make life a hundred times harder for scammers.
1. Types of Wallets and Their Differences
When it comes to storing cryptocurrencies, it’s essential to understand that there are two main types of wallets: custodial and non-custodial. The difference lies in who controls the private keys and, therefore, your funds.
Custodial Wallets
With these wallets, you rely on a third party, like an exchange, to hold your private keys, and thus, your tokens. It’s similar to a traditional bank account, where a bank manages your money and gives you access through its interface.
Pros of custodial wallets
1) User-friendliness. They often have user-friendly interfaces, making them appealing for beginners.
2) Account recovery. If you lose your login details, these wallets usually offer recovery options via your email or phone number.
Cons of custodial wallets
1) Risk of hacking. If an exchange is hacked, your funds could be stolen, as seen in the cases of Mt.Gox and Cryptopia.
2) Limited control. Since an exchange holds your keys, you don’t have full ownership of your assets. A company can freeze or restrict your access; for example, due to regulatory requests or if you forget to turn off a VPN. If an exchange is untrustworthy, they could misuse your assets, like what happened with FTX.
Non-Custodial Wallets
These wallets give you full control over your private keys and, by extension, your assets. Examples include MetaMask, Trust Wallet, Rabby, or hardware wallets like Ledger. In this case, no one except you has access to your funds, not exchanges, nor other protocols, unless you explicitly grant them permission (Approve).
Pros of non-custodial wallets
1) Full control. Only you manage your funds, and no one can interfere with your transactions.
2) Increased security. If you use a hardware wallet or implement strong security measures, it’s much harder for your assets to be stolen compared to exchange accounts.
Cons of non-custodial wallets
1) Key responsibility. Losing your private key or seed phrase means losing access to your wallet forever. There’s no recovery mechanism like with banks, so it’s crucial to write down your seed phrase and store it safely. We’ll discuss why paper is a better option later.
2) More complex management. For beginners, managing private keys and seed phrases can feel overwhelming and confusing.
Ultimately, choosing between custodial and non-custodial wallets comes down to how much you trust third parties and whether you’re ready to take full responsibility for your funds. There’s nothing wrong with CEXs, as they often have more liquidity than DEXs. Yet storing your assets on Web3 wallets is considered safer.
2. The Dangers of Approve & Permit2
In the Ethereum ecosystem and other blockchains that run on smart contracts, there’s a mechanism called Permit that allows users to sign transactions without sharing their private keys. This speeds up interactions with decentralized apps (dApps) and simplifies token management processes. However, this tool comes with its own risks.
What Is Permit2?
Permit2 is an upgraded version of the original Permit mechanism, designed to manage transaction permissions on the Ethereum blockchain and other compatible networks. Its main purpose is to let users authorize specific token operations without needing to sign every single transaction. This is convenient for frequent actions, like in Web3 games, where it cuts down on the need to confirm every small interaction.
Risks
The main risks come from mismanaging these permissions, which can open the door for hackers to access your tokens:
1) Unlimited permissions. Some users, trying to reduce transaction clutter, give smart contracts “infinite” permissions to use their tokens. This means the contract can access any amount of tokens at any time until the permission is revoked. If the contract gets hacked or compromised, your assets could be stolen.
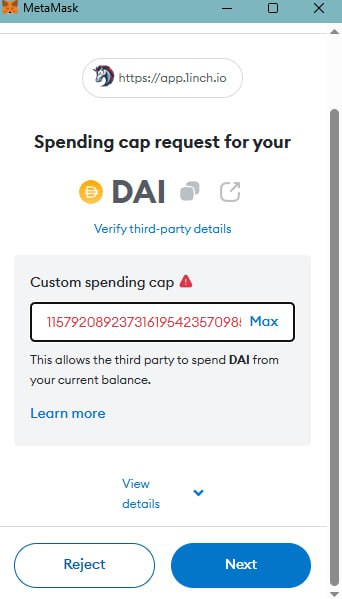
2) Fraudulent contracts. Scammers can create fake dApps or contracts that ask for permission to access your tokens. Once you grant it, they can move your funds to their own wallets.
3) Hidden vulnerabilities. Some contracts may have hidden bugs or exploits that hackers can use to transfer your tokens to scam addresses without your knowledge.
How to Protect Yourself?
To minimize risks associated with Permit2 and Approve, follow a few simple rules:
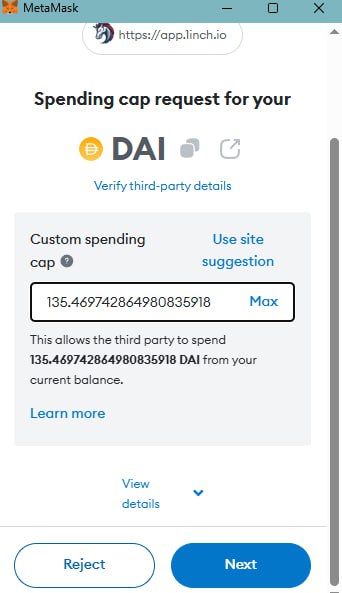
• Set limited permissions. Never grant smart contracts unlimited token access. Always specify limited amounts for each individual transaction. For instance, if you’re swapping 135 DAI for ETH, set the Approve transaction limit to 135 DAI.
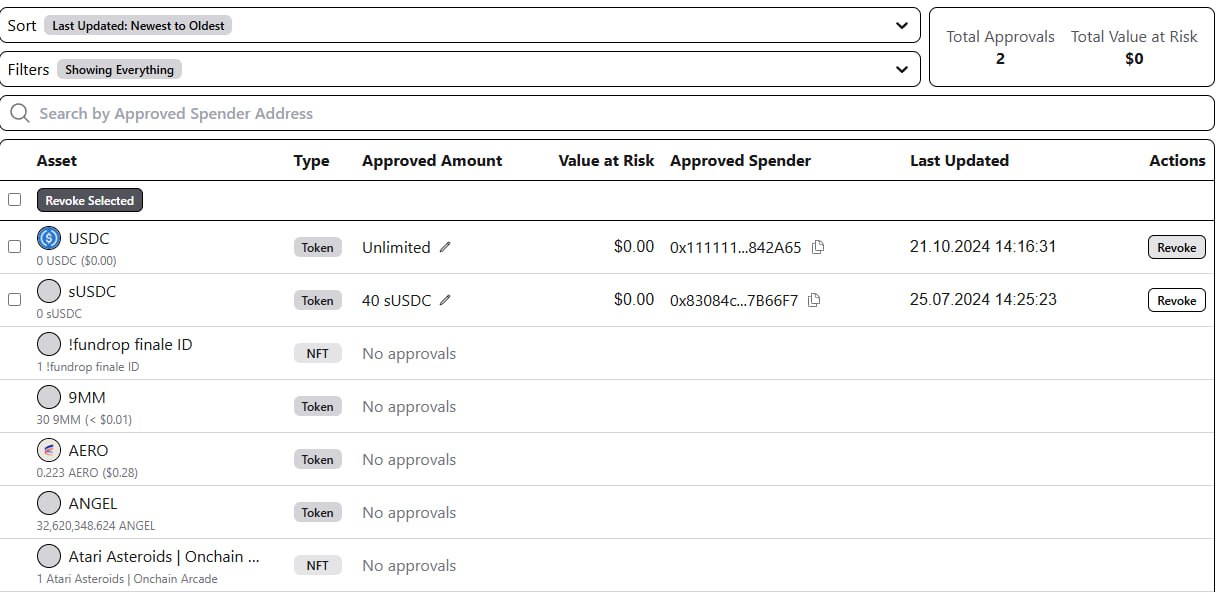
• Regular monitoring. Periodically check your active permissions with specialized tools like Etherscan or Revoke.cash. These let you quickly revoke any unnecessary or suspicious permissions.
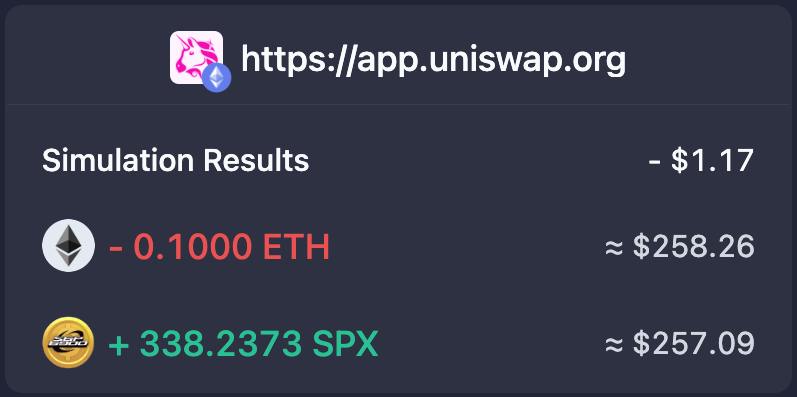
• Use wallets with transaction descriptions. Some wallets, like Rabby or Phantom, allow you to view an explanation of contract functions. Rabby even lets you revoke Approve permissions directly within the wallet, which is a huge plus for beginners.
• Stick to trusted dApps. Always verify and use only reputable, popular dApps. Avoid unfamiliar or newly launched projects. If you’re participating in testnets or other programs for new blockchains, it’s best to set up a separate wallet with no assets in it.
3. Phishing
Phishing in crypto often starts with a fake message. This could be an email, a message in a chat app, or a fake notification supposedly from an official website. The aim is to trick users into clicking on a malicious link or connecting their wallet and signing a transaction on a fraudulent site.
Recently, many projects (especially those nearing a TGE) face social media hacks that result in fake links to an “airdrop.” These messages usually include phrases like “limited time only,” “claim your reward now,” or “grab the drop within 2 hours.” Scammers count on people’s FOMO (fear of missing out).
How to Avoid Phishing Attacks?
• Double-check URLs. Before clicking any link or connecting your wallet, make sure you’re on the official website by confirming through various sources. Projects often post links to their official sites on X (ex-Twitter), Medium, and Discord. Official sites can also be found on analytical platforms like CryptoRank. Carefully compare the URL, and only proceed if you’re sure it’s genuine.
• Don’t click on suspicious links. If you receive an unexpected offer from unknown senders via email or message, never click the link. Legitimate crypto companies will never ask for your private keys or other sensitive information.
• Verify recipient addresses. Before sending any funds, always check the address you’re sending to. Phishing websites can automatically replace the correct address with their own. A common trick is swapping the real address with a fake one that shares similar starting and ending characters with your wallet address.
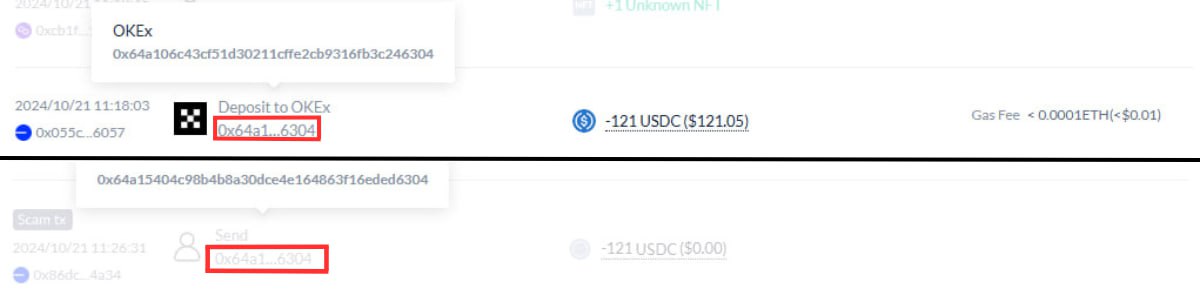
• Pressure and urgency. Scammers often try to create a sense of urgency, with messages like “Your account will be blocked!” or “Last chance to claim the airdrop!” This tactic is designed to push you into making a hasty decision without thinking it through.
• Requests for sensitive information. Legitimate services will never ask for your private keys, passwords, or seed phrases. Any such request is a clear sign you’re being scammed.
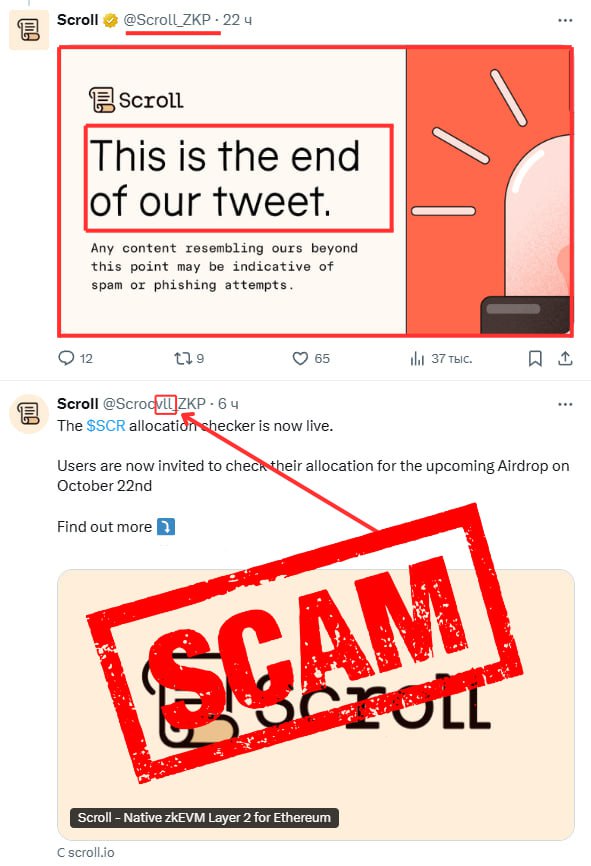
• Always verify a project’s @username on X (ex-Twitter). A common phishing technique involves fake X accounts “continuing” an original account’s thread in the comments, often including a link to a phishing article or airdrop. Scammers try to mimic usernames as closely as possible. For instance, they might use “@SuiNethwork,” “@SiuNetwork,” or “@SuiNetvork” to imitate Sui’s official account (@SuiNetwork). Most projects end their threads with a tweet noting it’s the final one, but it’s essential to double-check.
4. Rug Pull & Honeypot
Imagine coming across a promising sale for a cutting-edge token like “PUPKINO” that claims to solve all crypto problems with a revolutionary mega-blockchain, but the team collects funds through an IDO (Initial DEX Offering). You invest your hard-earned $1,000, but after the token presale, the project’s X and Discord vanish. This is a classic rug pull scam, where project devs disappear with investors’ funds, leaving behind worthless tokens.
Signs of a Rug Pull and How to Avoid Such Projects
• Unverified team. If developers don’t disclose their real names or background info, this is the very first red flag. A reputable team should be transparent, with LinkedIn and X accounts.
• Too-good-to-be-true promises. If a project guarantees huge profits in a short time, it’s probably a scam. Remember, there are no “guaranteed” returns in crypto, especially with new projects.
• Recently created accounts and channels. Check the creation date of project accounts. Recently registered accounts with minimal information or followers can be a sign of fraud.
• Lack of investment from funds. Most reputable funds have analytical teams that filter projects before investing. If no established funds have invested, it’s best to pass on it.
• No open code or documentation. Credible crypto projects publish their code on GitHub and provide documentation (a white paper) for review. If a project hides these details or offers no technical information, it’s a warning sign.
A honeypot is another common scam, particularly dangerous for newcomers. Unlike phishing or rug pulls, where scammers simply take your money, a honeypot traps users in a way that appears legitimate at first. When you attempt to exchange these tokens, however, you’ll find it’s impossible to do so.
The basic setup of this scam involves creating a fake smart contract or token that attracts users with the promise of quick profits (especially common with meme tokens). But as soon as users try to trade or interact with the token, they realize they can’t withdraw their funds due to contract code limitations. It might look like a tech issue, insufficient gas fees, or a minor delay, but the contract is deliberately designed to block fund withdrawals. In the smart contract, it’s pre-coded that tokens can only be bought, not sold. Once enough people buy in, scammers drain liquidity.
How to Recognize a Honeypot?
• Check smart contracts. Always review the smart contract code you interact with using platforms like Etherscan or BscScan. If you notice restrictions on withdrawals or token sales, it’s a bad sign.
• Be cautious with low-liquidity tokens. If a token has low liquidity and is only available on one or two small exchanges, it may be a scam. Ensure the token has adequate liquidity using tools like DexScreener or DexTools.
• Research a project. Honeypots may pose as promising new projects. Always investigate the project team, their reputation, and whether they provide open-source code.
• Use specialized tools for verification. There are tools designed to identify potential honeypots, such as Honeypot.is, which allows you to verify if a token or contract is likely fraudulent.
5. Scams via Telegram
You’ve probably received direct messages with offers for “testing mainnets,” “working with official partner exchanges,” “jobs in trading companies,” “earning passive income,” and so on. Scammers typically create fake accounts, use a profile picture of a suave guy in a suit, and start spamming your DMs. Those who fall for it might send them a supposed $100, and then the scammers either disappear or give their victims back $200. The victim believes them and then sends $1,000 to the scammers, after which they vanish for good.
Besides, on Telegram, scammers can send various PDF files or ZIP archives that automatically download to your device (this feature is enabled by default in Telegram settings). These files might be disguised as books, courses, video lessons, or simply labeled with generic names like “Documents.” As soon as you open one of these, malware can infect your device, stealing all your data, including your wallet’s private keys.
With the hype around meme coins, Telegram bots for quick trading have gained momentum. Most popular bots require you to create a new wallet to which you can send tokens and then snipe. However, some bots ask you to import your private key, putting the imported wallet at enormous risk. It’s best to avoid such bots, and if you must use them, create a separate wallet where you don’t store your funds, as scammers with access to your private key can steal your tokens.
How to Avoid It?
• Don’t respond to strangers in messengers and immediately block them, marking them as spam.
• Never agree to easy money-making schemes; remember, there’s no such thing as a free lunch.
• Disable automatic file downloads in Telegram settings (Settings — Advanced Settings — Automatic Media Download).
• Never import your private keys into Telegram bots.
• Store your private keys and seed phrases on paper, not digitally.
6. The Dangers of OneDrive and Other Cloud Storage Services
Many users, not fully understanding the importance of protecting their private information, may store their seed phrases in insecure places, like text files, Excel spreadsheets, Notion, or cloud storage services such as OneDrive, Google Drive, or iCloud.
How Seed Phrases Get Stolen via Cloud Storage?
• Hacking cloud accounts. If your OneDrive or any other cloud account gets hacked, the perpetrators gain access to all the files stored there. If among those files is a document containing your seed phrase, hackers can access it. Even if the file is password-protected, a weak password can make your data vulnerable.
• Keyloggers. Scammers may use malware (like keyloggers) or phishing attacks to access your OneDrive account. If your device has malware installed, it can capture your logins and passwords for cloud storage, giving hackers full access to your files.
• Automatic data synchronization. Some users may not realize that their devices automatically sync important files to the cloud (this option is enabled by default on Windows). For example, when you create a document with your seed phrase on your PC, it might automatically upload to OneDrive through sync functions. This makes your seed phrase accessible online, increasing the risk of theft in case of hacking.
How to check if a scammer has access to your OneDrive?
-
Check what data is stored in the cloud.
-
Review successful login attempts to your account.
How to protect your seed phrases from cloud storage theft?
• Never store seed phrases and private keys in cloud services. This is a basic security rule. Ideally, your seed phrase should be kept offline. Use paper records stored in a secure, physically protected location (like a safe).
• Use hardware wallets. Hardware wallets (like Ledger or Trezor) offer a high level of security since private keys and seed phrases are never stored online.
• Avoid weak passwords. Create complex and unique passwords for each of your accounts. It’s best to use password managers that can generate and store secure passwords.
• Disable automatic synchronization. Ensure your device doesn’t automatically sync important files with the cloud without your knowledge. Check sync settings and disable it for important documents.
• Encrypt important files. If you must store any info in the cloud, make sure to encrypt it with a reliable encryption algorithm. However, note that even encrypted files can be vulnerable if a weak password is used.
Remember: In the crypto landscape, you’re responsible for your own funds. By following these simple rules and staying vigilant, you can protect your assets and avoid common mistakes.


