Fed Interest Rates: Goolsbee’s Crucial Warning on Inflation’s Stealthy Impact
BitcoinWorld
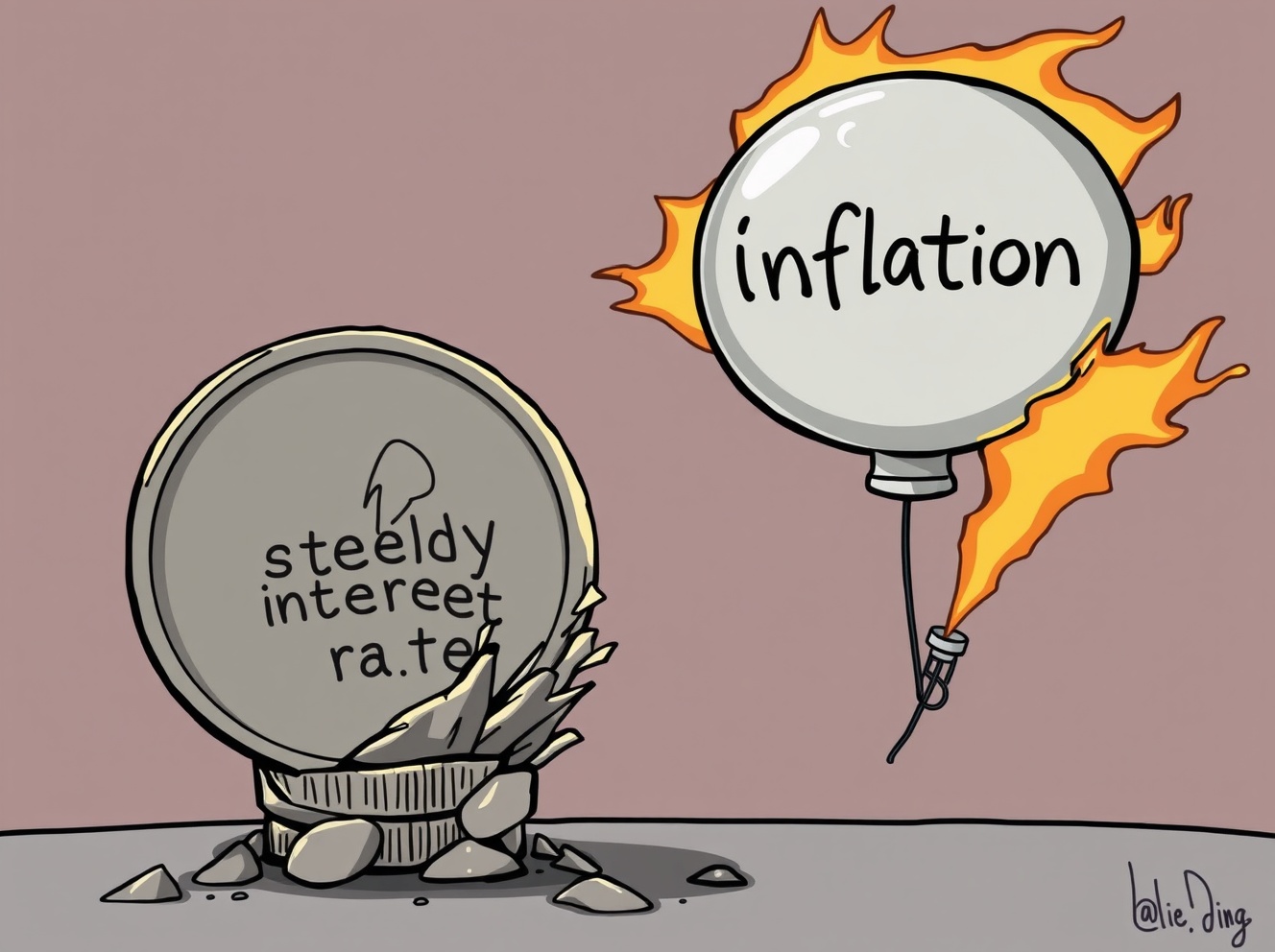
Fed Interest Rates: Goolsbee’s Crucial Warning on Inflation’s Stealthy Impact
Ever wondered how central bank decisions impact your wallet, even when nothing seems to change? Chicago Federal Reserve President Austan Goolsbee recently issued a significant warning about Fed interest rates. He stated that keeping these rates stable while inflation continues to rise is essentially the same as an interest rate cut. This might sound counterintuitive, but it carries crucial implications for the economy and everyone’s financial well-being.
What Does “Holding Steady” with Fed Interest Rates Really Mean for You?
When the Federal Reserve sets Fed interest rates, it influences the cost of borrowing money across the entire economy. Typically, raising rates makes borrowing more expensive, which slows down spending and helps cool inflation. Conversely, cutting rates makes borrowing cheaper, stimulating economic activity. Goolsbee’s perspective highlights a subtle but powerful economic dynamic.
- The Erosion of Value: If inflation is climbing—meaning your money buys less than it did before—and interest rates aren’t adjusted upwards to compensate, the real value of those rates diminishes. It’s like running on a treadmill that’s speeding up; if you don’t increase your pace, you’re effectively falling behind.
- Real vs. Nominal Rates: To grasp this, consider “real” versus “nominal” interest rates. Nominal rates are the advertised rates you see. Real rates, however, account for inflation. If nominal rates remain constant but inflation rises, real interest rates effectively fall. This makes borrowing relatively cheaper in real terms for individuals and businesses.
- An Unintended Stimulus: This effective reduction in real interest rates can inadvertently stimulate economic activity, mirroring the effect of an actual rate cut. Such a stimulus, in an already inflationary environment, risks further fueling price increases, creating a challenging and potentially self-perpetuating cycle.
How Do Unchanged Fed Interest Rates Fuel Inflation’s Fire?
The implications of such a scenario are far-reaching, affecting various facets of the economy. When Fed interest rates don’t keep pace with inflation, several economic dynamics come into play:
- Declining Purchasing Power: Consumers find their hard-earned money losing value faster. If wages don’t keep up with rising prices, households experience a real decrease in purchasing power. This can lead to financial strain and reduced living standards.
- Skewed Investment Decisions: Businesses might perceive borrowing as cheaper due to lower real interest rates. This could encourage increased borrowing and investment, potentially leading to over-investment or even misallocation of capital in an economy already grappling with overheating.
- Risk of Asset Bubbles: Persistently low real rates can contribute to asset price inflation. The value of assets like stocks, real estate, and even cryptocurrencies might rise rapidly, potentially creating speculative bubbles that pose risks to financial stability if they burst.
- Erosion of Savings: For individuals relying on savings, steady nominal interest rates mean their wealth is slowly eroding in real terms. The returns on their savings accounts or fixed-income investments simply don’t outpace inflation, discouraging prudent saving habits and pushing some towards riskier ventures.
This situation presents a significant challenge for the Federal Reserve as it strives to achieve its crucial dual mandate: maintaining maximum employment while ensuring price stability.
What’s the Fed’s Next Move Amidst This Crucial Challenge to Fed Interest Rates?
The Federal Reserve faces a delicate balancing act. Aggressively raising Fed interest rates could risk tipping the economy into a recession, potentially leading to job losses and reduced economic output. However, not acting decisively enough against persistent inflation could allow it to become entrenched, making it much harder and more painful to control in the long run.
Policymakers must carefully analyze a wide array of economic data, including employment figures, consumer spending, and global economic trends, to determine the most appropriate course of action. This involves looking beyond just the headline inflation numbers and understanding the underlying drivers of price increases. The ultimate goal is to ensure that monetary policy remains sufficiently restrictive to bring inflation back down to its target level without causing undue economic hardship or instability.
In essence, Austan Goolsbee’s warning serves as a stark reminder: when it comes to monetary policy, appearances can be deceiving. Steady Fed interest rates might seem like a neutral stance, but in an environment of rising inflation, they can inadvertently contribute to the very problem they are meant to combat. This highlights the ongoing complexities and crucial decisions facing central banks worldwide in their quest for lasting economic stability.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1: What is Chicago Fed President Austan Goolsbee’s main concern about Fed interest rates?
A1: Goolsbee is concerned that keeping nominal Fed interest rates stable while inflation is rising effectively acts as an interest rate cut, inadvertently stimulating the economy and potentially worsening inflation.
Q2: How does inflation affect the real value of interest rates?
A2: Inflation erodes the purchasing power of money. If nominal interest rates don’t increase to match or exceed inflation, the real (inflation-adjusted) interest rate falls, meaning the return on savings or the cost of borrowing becomes effectively lower.
Q3: What are the economic consequences of steady rates amid rising inflation?
A3: Consequences include declining consumer purchasing power, potentially skewed investment decisions by businesses, the risk of asset bubbles, and the erosion of savings, all of which can destabilize the economy.
Q4: Why is the Federal Reserve’s decision-making so challenging right now?
A4: The Fed faces a difficult balance: raising rates too much risks a recession, while not raising them enough could entrench inflation. They must navigate these risks to achieve both maximum employment and price stability.
Q5: How can individuals protect their savings during inflationary periods?
A5: While not financial advice, strategies often include diversifying investments, considering inflation-protected securities (like TIPS), or exploring assets that historically perform well during inflation, always consulting with a financial advisor.
Did you find this analysis insightful? Share Goolsbee’s crucial warning with your network and spark a conversation about the future of our economy and the impact of Fed interest rates. Your insights can help others understand these complex financial dynamics!
To learn more about the latest monetary policy trends, explore our article on key developments shaping the global economy and its future outlook.
This post Fed Interest Rates: Goolsbee’s Crucial Warning on Inflation’s Stealthy Impact first appeared on BitcoinWorld.
Read More

Trump faces legal block in firing campaign against Fed official
Fed Interest Rates: Goolsbee’s Crucial Warning on Inflation’s Stealthy Impact
BitcoinWorld

Fed Interest Rates: Goolsbee’s Crucial Warning on Inflation’s Stealthy Impact
Ever wondered how central bank decisions impact your wallet, even when nothing seems to change? Chicago Federal Reserve President Austan Goolsbee recently issued a significant warning about Fed interest rates. He stated that keeping these rates stable while inflation continues to rise is essentially the same as an interest rate cut. This might sound counterintuitive, but it carries crucial implications for the economy and everyone’s financial well-being.
What Does “Holding Steady” with Fed Interest Rates Really Mean for You?
When the Federal Reserve sets Fed interest rates, it influences the cost of borrowing money across the entire economy. Typically, raising rates makes borrowing more expensive, which slows down spending and helps cool inflation. Conversely, cutting rates makes borrowing cheaper, stimulating economic activity. Goolsbee’s perspective highlights a subtle but powerful economic dynamic.
- The Erosion of Value: If inflation is climbing—meaning your money buys less than it did before—and interest rates aren’t adjusted upwards to compensate, the real value of those rates diminishes. It’s like running on a treadmill that’s speeding up; if you don’t increase your pace, you’re effectively falling behind.
- Real vs. Nominal Rates: To grasp this, consider “real” versus “nominal” interest rates. Nominal rates are the advertised rates you see. Real rates, however, account for inflation. If nominal rates remain constant but inflation rises, real interest rates effectively fall. This makes borrowing relatively cheaper in real terms for individuals and businesses.
- An Unintended Stimulus: This effective reduction in real interest rates can inadvertently stimulate economic activity, mirroring the effect of an actual rate cut. Such a stimulus, in an already inflationary environment, risks further fueling price increases, creating a challenging and potentially self-perpetuating cycle.
How Do Unchanged Fed Interest Rates Fuel Inflation’s Fire?
The implications of such a scenario are far-reaching, affecting various facets of the economy. When Fed interest rates don’t keep pace with inflation, several economic dynamics come into play:
- Declining Purchasing Power: Consumers find their hard-earned money losing value faster. If wages don’t keep up with rising prices, households experience a real decrease in purchasing power. This can lead to financial strain and reduced living standards.
- Skewed Investment Decisions: Businesses might perceive borrowing as cheaper due to lower real interest rates. This could encourage increased borrowing and investment, potentially leading to over-investment or even misallocation of capital in an economy already grappling with overheating.
- Risk of Asset Bubbles: Persistently low real rates can contribute to asset price inflation. The value of assets like stocks, real estate, and even cryptocurrencies might rise rapidly, potentially creating speculative bubbles that pose risks to financial stability if they burst.
- Erosion of Savings: For individuals relying on savings, steady nominal interest rates mean their wealth is slowly eroding in real terms. The returns on their savings accounts or fixed-income investments simply don’t outpace inflation, discouraging prudent saving habits and pushing some towards riskier ventures.
This situation presents a significant challenge for the Federal Reserve as it strives to achieve its crucial dual mandate: maintaining maximum employment while ensuring price stability.
What’s the Fed’s Next Move Amidst This Crucial Challenge to Fed Interest Rates?
The Federal Reserve faces a delicate balancing act. Aggressively raising Fed interest rates could risk tipping the economy into a recession, potentially leading to job losses and reduced economic output. However, not acting decisively enough against persistent inflation could allow it to become entrenched, making it much harder and more painful to control in the long run.
Policymakers must carefully analyze a wide array of economic data, including employment figures, consumer spending, and global economic trends, to determine the most appropriate course of action. This involves looking beyond just the headline inflation numbers and understanding the underlying drivers of price increases. The ultimate goal is to ensure that monetary policy remains sufficiently restrictive to bring inflation back down to its target level without causing undue economic hardship or instability.
In essence, Austan Goolsbee’s warning serves as a stark reminder: when it comes to monetary policy, appearances can be deceiving. Steady Fed interest rates might seem like a neutral stance, but in an environment of rising inflation, they can inadvertently contribute to the very problem they are meant to combat. This highlights the ongoing complexities and crucial decisions facing central banks worldwide in their quest for lasting economic stability.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1: What is Chicago Fed President Austan Goolsbee’s main concern about Fed interest rates?
A1: Goolsbee is concerned that keeping nominal Fed interest rates stable while inflation is rising effectively acts as an interest rate cut, inadvertently stimulating the economy and potentially worsening inflation.
Q2: How does inflation affect the real value of interest rates?
A2: Inflation erodes the purchasing power of money. If nominal interest rates don’t increase to match or exceed inflation, the real (inflation-adjusted) interest rate falls, meaning the return on savings or the cost of borrowing becomes effectively lower.
Q3: What are the economic consequences of steady rates amid rising inflation?
A3: Consequences include declining consumer purchasing power, potentially skewed investment decisions by businesses, the risk of asset bubbles, and the erosion of savings, all of which can destabilize the economy.
Q4: Why is the Federal Reserve’s decision-making so challenging right now?
A4: The Fed faces a difficult balance: raising rates too much risks a recession, while not raising them enough could entrench inflation. They must navigate these risks to achieve both maximum employment and price stability.
Q5: How can individuals protect their savings during inflationary periods?
A5: While not financial advice, strategies often include diversifying investments, considering inflation-protected securities (like TIPS), or exploring assets that historically perform well during inflation, always consulting with a financial advisor.
Did you find this analysis insightful? Share Goolsbee’s crucial warning with your network and spark a conversation about the future of our economy and the impact of Fed interest rates. Your insights can help others understand these complex financial dynamics!
To learn more about the latest monetary policy trends, explore our article on key developments shaping the global economy and its future outlook.
This post Fed Interest Rates: Goolsbee’s Crucial Warning on Inflation’s Stealthy Impact first appeared on BitcoinWorld.
Read More

